Equity Calculation
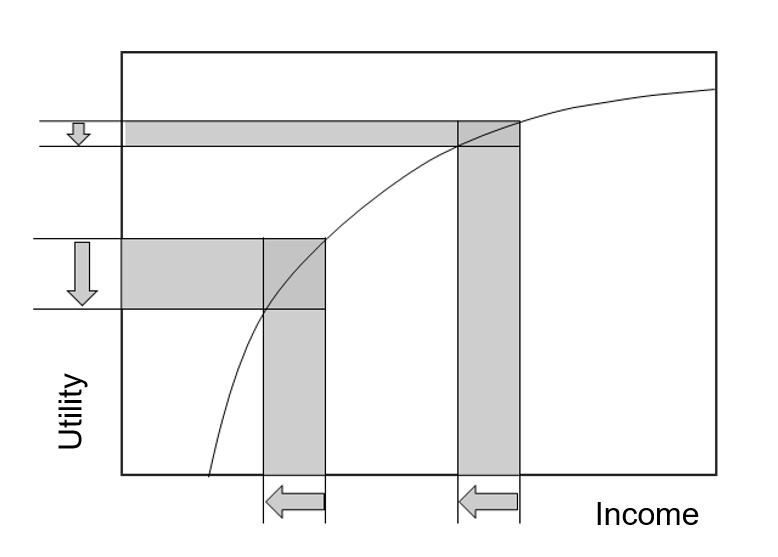
Equity methods seek to compensate for the unfair distribution in income when calculating flood damages. They rely on the concept of marginal utility of income, which holds that a loss of $1 for a rich person is not equivalent to the loss of $1 for a poor person. Utility is defined in economics as the satisfaction, usefulness, or happiness derived from - in this case - income. Equity weights are a way to correct for the inequality in marginal utility across income classes. Essentially, the equity weight represents the relative size of the marginal utility (a loss in utility due to a change in income - brought on in this case by flood damages) compared to the marginal utility for the community’s average income level. This leads to equity weights greater than 1 for incomes below average, and less than 1 for higher-than-average incomes. The equity weights are then used as a multiplicative factor on flood damages.
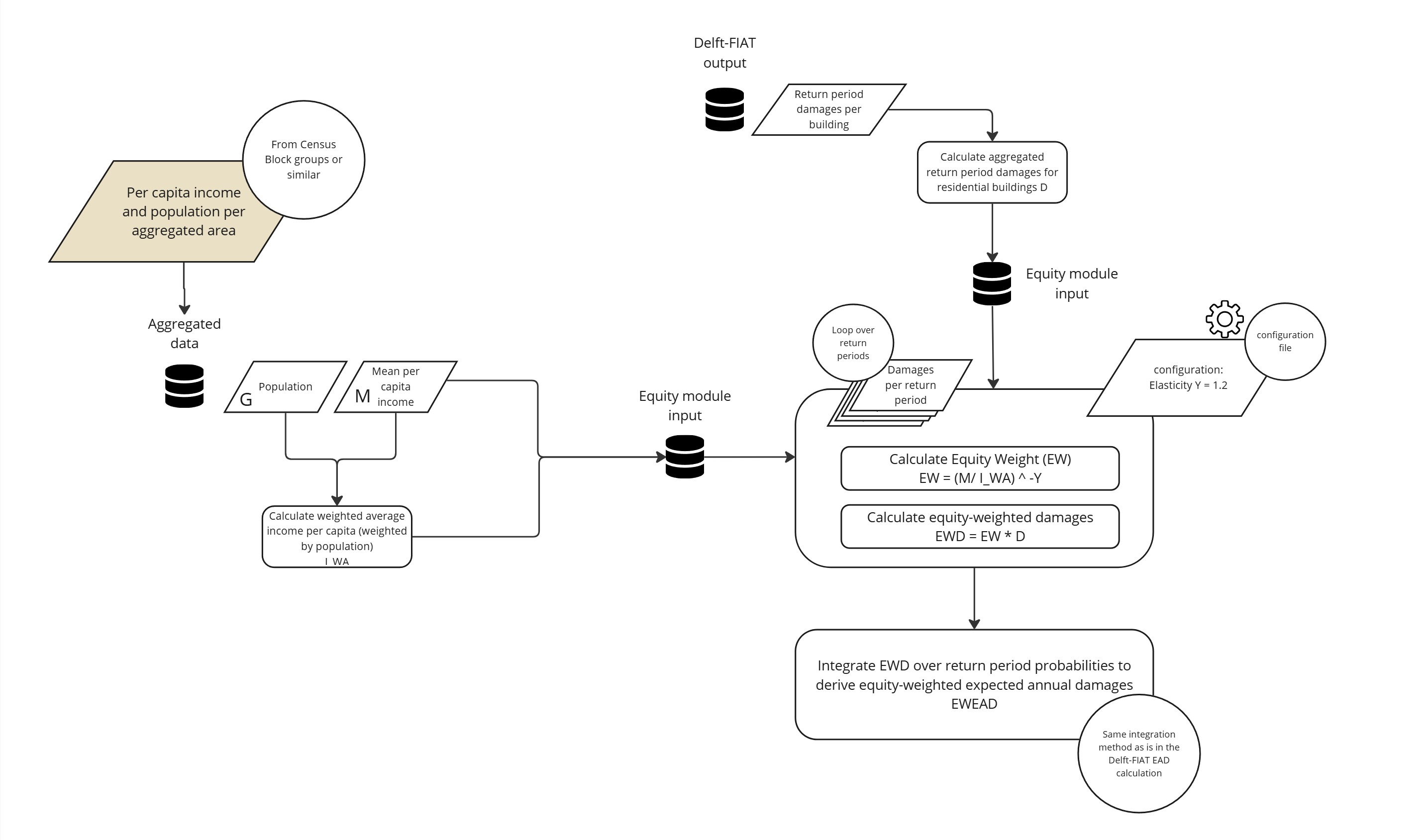
FloodAdapt includes a module which automatically calculates equity weights and applies them to risk estimates, using methods described in literature (1). The calculation framework of the module is depicted in Figure 2.
Inputs to the method are:
Mean per capita income (\(M\)) and population \((P)\) at aggregated scale, for example census block groups. This information can be obtained automatically when setting up the Delft-FIAT model
Return period damages per building \(D\) (output from the impact module in a risk calculation).
The module then does the following:
Calculates the weighted average income per capita, weighted by population \(I_{WA} = \frac{\sum (M_i \cdot P_i)}{P}\), where \(i\) represents the areas, for example census block groups.
Derives the equity weight for each aggregated area: \(EW_i = \left(\frac{M_i}{I_{WA}}\right)^\gamma\). Note that \(\gamma\) is set to 1.2. This parameter is expected to be made configurable by FloodAdapt users in future releases.
Calculates for each return period \(j\) the equity-weighted damages per aggregation area \(EWD_{i,j} = EW_i \cdot D_{i,j}\)
Integrates the equity-weighted damages over the return periods using log-linear interpolation to derive the equity-weighted expected annual damages for each aggreagation area.