Setting up a SFINCS model
SFINCS is an open-source model for simulating compound flooding that can be integrated into the FloodAdapt platform. To set up FloodAdapt in a new location, you first need to create a SFINCS model for the project area. This initial model, called the “baseline” SFINCS model, can then modified through FloodAdapt’s user interface to simulate scenarios such as hurricanes or synthetic events, and include future conditions like sea level rise.
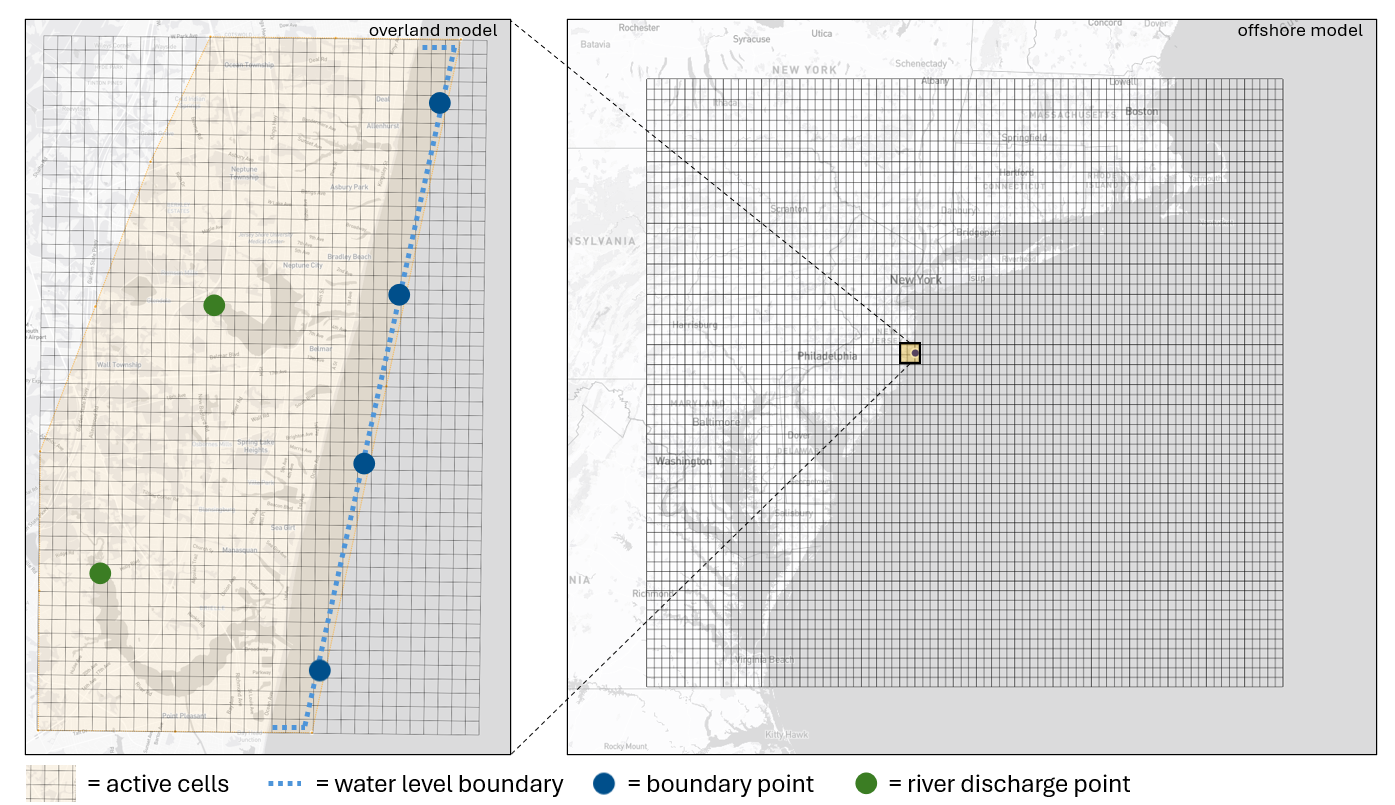
SFINCS is designed to simulate compound flooding caused by various drivers, including storm surge, tides, rainfall, and river discharge (Figure 1). A fully functional FloodAdapt setup typically includes two SFINCS models:
Offshore model: Simulates large-scale storm surge events, like hurricanes, and propagates the surge toward the area of interest.
Overland model: Uses water level data from the offshore model to simulate flooding over the land via a process called “grid nesting”.
In some scenarios (e.g., historical events with gauged water levels or synthetic events), the offshore model isn’t required. Instead, tide gauge data or synthetic water level signals are directly imposed at the overland model’s water level boundary.
Components of a SFINCS Model
A SFINCS model is comprised of three key components:
Model grid: The spatial framework for simulations.
Topography and bathymetry data: These are mapped to the grid to define the terrain and underwater features.
Initial and boundary conditions: Describe starting water levels and how they change over time at model boundaries (or throughout the domain with respect to rainfall, or at a source point with respect to river discharge).
Using this information, SFINCS calculates water levels within the model boundaries and saves the maximum inundation results mapped throughout the model area and time series of water levels at selected points.
The SFINCS Model-Builder tool simplifies the creation of SFINCS models for FloodAdapt. It allows users to:
- Create the model grid
- Map topography and bathymetry data to the grid
- Define active cells
- Define the water level boundaries
- Define boundary points for offshore-overland model communication
- Define discharge points for river discharge
Figure 2 is a schematic overview of the SFINCS model components:
SFINCS Data Requirements
After installing the FloodAdapt Model-Builder, the following folder structure is created:
├───📁 FloodAdaptModelBuilder/
|
├───📁 _internal/
|
├───📁 data/
│ │
| ├───📁 topobathy/
| │ └───📄 dem.tif
| └───📁 watersheds/
| └───📄 watersheds.gpkg
|
├───🔵 FloodAdaptModelBuilder.exe
|
├───🔵 unins000.dat
|
└───🔵 unins000.exeFor full functionality, users must provide:
- DEM (Digital Elevation Model): a
.tiffile nameddem.tifin thetopobathyfolder. - Watersheds Geopackage: A
.gpkgfile namedwatersheds.gpkgin thewatershedsfolder.
For detailed instructions on creating a SFINCS model using the Model-Builder tool, continue to the SFINCS model-builder documentation.