Events
FloodAdapt allows users to specify and simulate the flooding and impacts for many different types of (compound) events. These can be either historically-based or synthetic events. The historically-based events use historical water levels or hurricane tracks, but allow users to modify event specifics to create what-if event scenarios, for example by adding or intensifying rainfall or shifting a hurricane track.
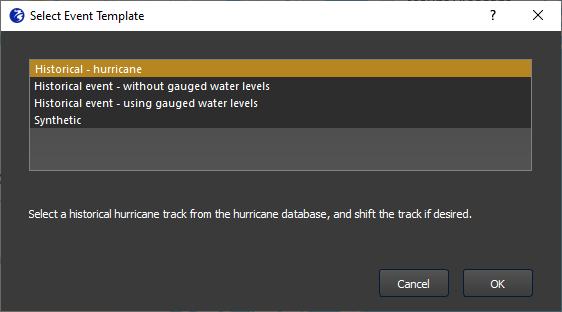
There are three historically-based event types, which are described in the coming sections:
- Historical hurricane
- Historical event with gauged water levels
- Historical event without gauged water levels
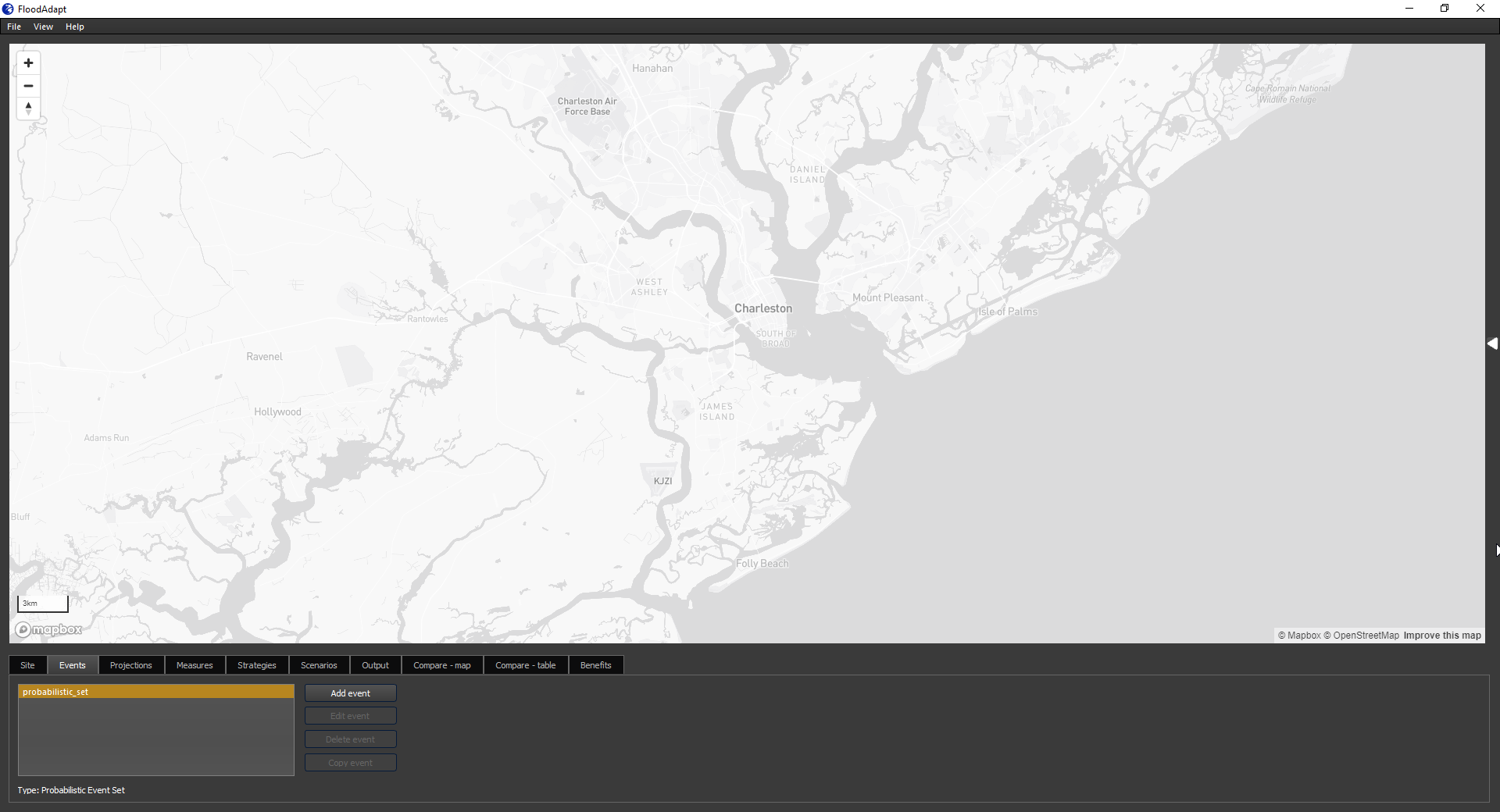
To create an event, the user goes to the Events tab in FloodAdapt (see Figure 1). Prior to creating any events, there may be one event already shown in the event list window. This will be a probabilistic event set that is prepared as part of system setup, and is used to calculate risk. Underneath the event set window, the event “Type” is indicated. For event sets this will say “Probabilistic Event Set.” For events that you create in the Events tab, these will say “Single Event”. Next to the event list window there are buttons to add, edit, delete, and copy an event. Prior to creating any events, only the “Add event” button will be active.
When a user clicks Add event in the event window, they will be prompted to choose from one of the three historical event types or the synthetic event type. Each selection opens a window where the user can specify event information.
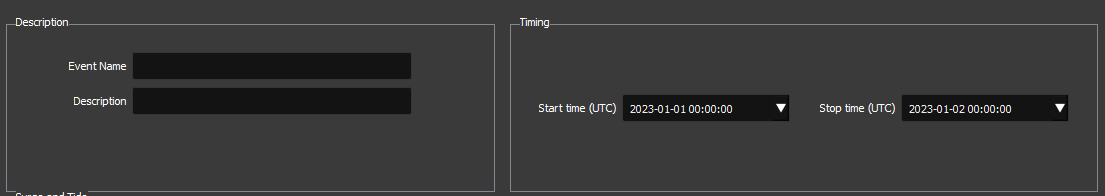
Each event type will have unique input that is required, but they also share some common input. The user must provide an event name, and - optionally - a description. Additionally, all historic events require a start and stop time of the event.
Event names must be unique and cannot have any spaces or special characters (underscores are allowed). Event descriptions are optional and have no syntax restrictions. For example, an event name could be KingTideNov2021, and the long name could be King Tide - November 2021.
The format for the start and stop time is ‘YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss’, where YYYY = four-digit year, MM = two digit month, DD = two-digit day, hh = two-digit hour, mm = two-digit minutes, and ss = two-digit seconds. The user can type in a date, or select a date from a drop-down calendar.
How are events modeled in FloodAdapt?
FloodAdapt supports two levels of hydrodynamic models:
An offshore model that calculates nearshore water levels based on astronomic tides, wind fields and pressure fields. These nearshore water levels are used to force the overland model.
An overland model that calculates the inundation over land due to nearshore water levels, local wind, rainfall, and river discharge.
When a user selects a historical hurricane, FloodAdapt will pull in wind and pressure information about the track, and use this information to generate wind and pressure fields using the Holland 2010 method. It also uses the track information to estimate the rainfall field using the IPET method. The wind, pressure, and rainfall fields are used by the offshore model to calculate nearshore water levels. These are then used, together with the same wind, pressure and rainfall fields, to run the overland flood model.
When a user selects a Historical event with gauged water levels, only the overland model will be run, using the gauged water levels as input to the overland model.
When a user selects a Historical event without gauged water levels, the offshore model will first be run using the wind and pressure data from the NOAA Global Forecast System (GFS). The calculated nearshore water levels will then be input to the overland model to calculate the overland flooding.
When a user selects a Synthetic event, only the overland model will be run, using the tide, surge, rainfall, wind, and river discharge information specified by the user.